Geothermal Energy in the US: Powering the Future with Earth’s Heat

Geothermal energy in the US represents a significant, largely untapped resource for sustainable power generation, offering a consistent and reliable alternative to fossil fuels by harnessing the Earth’s internal heat to power homes and businesses.
Imagine a world powered by the very ground beneath our feet. Geothermal energy in the US: Unlocking the Potential of Underground Heat to Power Homes and Businesses is not just a futuristic dream, but a tangible solution gaining traction as we seek sustainable alternatives.
The Earth’s Boiler Room: What is Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal energy, quite simply, is the heat from within the Earth. This thermal energy is contained in the rock and fluids beneath the Earth’s crust and can be tapped into for heating and electricity production. It’s a resource constantly replenished by the planet itself.
Unlike solar or wind power, geothermal energy is available 24/7, regardless of weather conditions. This reliability makes it an attractive option for baseload power, meaning it can provide a constant source of energy to meet continuous demand.
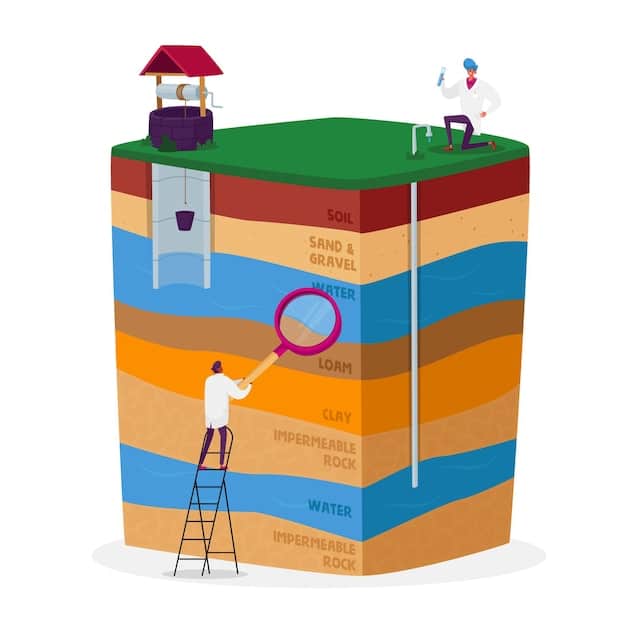

Types of Geothermal Resources
Geothermal resources can be categorized based on temperature and geological characteristics. High-temperature resources are typically used for electricity generation, while low-temperature resources are suitable for direct-use applications such as heating and aquaculture.
- Hydrothermal Resources: These involve naturally occurring reservoirs of steam or hot water that can be directly tapped into.
- Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS): EGS involves creating artificial reservoirs by fracturing hot, dry rocks and injecting water to extract heat.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps (GHPs): GHPs utilize the shallow ground’s constant temperature to heat and cool buildings via a heat exchange system.
Geothermal energy offers a sustainable and dependable energy source with the potential to significantly reduce our carbon footprint and enhance energy security.
Geothermal Energy Potential in the US: A Sleeping Giant?
The US holds vast geothermal resources, particularly in the western states. However, the potential of this resource remains largely untapped due to various technical, economic, and regulatory challenges.
According to the US Geological Survey, the total geothermal resource base in the US is estimated to be over 3,000 gigawatts (GW), enough to power the entire country several times over. The challenge lies in effectively and economically harnessing this resource.
Geographic Distribution of Geothermal Resources
Geothermal resources are not evenly distributed across the US. The western states, particularly California, Nevada, Utah, and Oregon, have the highest potential for conventional hydrothermal resources. However, EGS technology could potentially unlock geothermal resources in other regions as well.
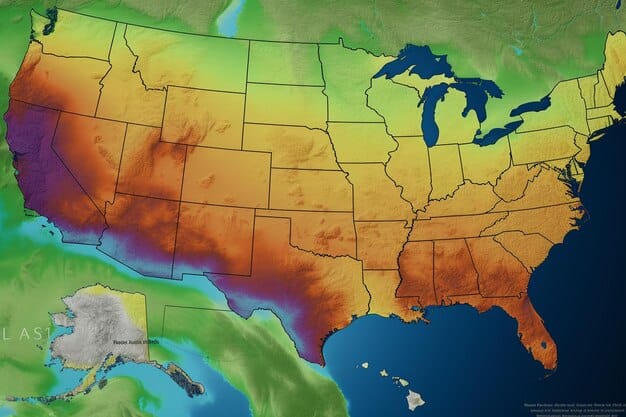
- California: Home to The Geysers, the world’s largest geothermal power plant, and has significant potential for further development.
- Nevada: Possesses abundant geothermal resources, with numerous operating power plants and promising EGS prospects.
- Utah and Oregon: Feature diverse geothermal resources, including hydrothermal systems and areas suitable for direct-use applications.
The vast geothermal resources in the US offer a significant opportunity to diversify the energy mix and move towards a more sustainable energy future.
Current Geothermal Energy Projects in the US: A Snapshot
While geothermal energy currently contributes a relatively small portion of the US electricity supply, several ongoing projects and initiatives are aimed at expanding its role. These projects range from new power plant developments to innovative direct-use applications.
As of 2023, the US has a total installed geothermal capacity of around 3.7 GW, primarily located in the western states. Several new projects are in various stages of development, with a focus on utilizing EGS technology to access previously unrecoverable resources.
Notable Geothermal Projects
Several key projects are driving the advancement of geothermal energy in the US. These projects showcase the diversity of geothermal applications and the potential for future growth.
The US Department of Energy (DOE) is actively supporting research and development efforts, including projects focused on EGS, advanced drilling technologies, and enhanced resource assessment. These investments are crucial for reducing the cost and risk associated with geothermal development.
- FORGE (Frontier Observatory for Research in Geothermal Energy): A dedicated research site focused on EGS technology, located in Utah.
- Raft River Geothermal Project: An EGS project in Idaho aimed at demonstrating the viability of accessing geothermal resources in previously unproductive areas.
- Geothermal Greenhouse Partnership: Direct-use applications in various states, utilizing geothermal heat for agricultural purposes.
These projects demonstrate the ongoing efforts to advance geothermal technology and expand its application across various sectors.
Benefits of Geothermal Energy: A Sustainable Solution
Geothermal energy offers numerous environmental, economic, and social benefits, making it a key component of a sustainable energy future. Its reliability, low emissions, and potential for local economic development contribute to its appeal.
Unlike fossil fuels, geothermal energy produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Geothermal power plants typically release only a small fraction of the CO2 emissions compared to coal or natural gas plants. Additionally, geothermal energy is a renewable resource, constantly replenished by the Earth’s internal heat.
Environmental and Economic Advantages
The environmental benefits of geothermal energy extend beyond reduced emissions. Geothermal power plants have a small land footprint compared to other energy sources. Direct-use applications, such as geothermal heating and cooling, can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs for homeowners and businesses.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Geothermal energy significantly reduces CO2 emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Small Land Footprint: Geothermal power plants require relatively little land.
- Energy Security: Geothermal resources are domestically available, reducing reliance on foreign energy sources.
Geothermal energy offers a compelling solution for mitigating climate change, enhancing energy security, and fostering local economic growth.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Path Forward
Despite its numerous benefits, geothermal energy development faces several challenges, including high upfront costs, technical complexities, and regulatory hurdles. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for unlocking the full potential of geothermal energy in the US.
The initial investment required to develop geothermal projects can be substantial, particularly for EGS projects that require drilling deep into the Earth. Additionally, geothermal development can be complex and requires specialized expertise, including geology, engineering, and environmental science.
Addressing the Barriers
Addressing the challenges will require a multi-faceted approach, including technological innovation, policy support, and public awareness. Continued research and development efforts are essential for reducing costs and improving the efficiency of geothermal technologies.
Government incentives, such as tax credits and loan guarantees, can help offset the high upfront costs of geothermal projects. Streamlining the permitting process and clarifying regulatory frameworks can also facilitate geothermal development.
- Technological Innovation: Advancements in drilling technologies and EGS techniques can reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Policy Support: Government incentives and streamlined regulations can encourage geothermal development.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the benefits of geothermal energy can increase support for its development.
By addressing these challenges, the US can unlock the vast potential of geothermal energy and create a more sustainable energy future.
The Future of Geothermal Energy in the US: Innovations and Growth
The future of geothermal energy in the US is bright, with ongoing research and development efforts paving the way for technological breakthroughs and increased deployment. Innovations in EGS, advanced drilling techniques, and hybrid geothermal systems are expected to drive future growth.
EGS technology holds immense potential for expanding the geographic availability of geothermal energy. By creating artificial reservoirs in hot, dry rocks, EGS can unlock geothermal resources in regions that lack natural hydrothermal systems. Advanced drilling techniques, such as directional drilling and closed-loop systems, are improving access to geothermal resources and reducing environmental impacts.
Emerging Trends
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of geothermal energy. These include the integration of geothermal energy with other renewable energy sources, the use of geothermal energy for energy storage, and the development of novel geothermal applications.
Hybrid geothermal systems, which combine geothermal energy with solar or wind power, can provide a more reliable and cost-effective energy supply. Geothermal energy can also be used for energy storage by pumping water underground and storing it for later use. Novel geothermal applications, such as mineral extraction and carbon sequestration, are also being explored.
- Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS): EGS is poised to unlock vast geothermal resources in previously inaccessible regions.
- Hybrid Systems: Integrating geothermal energy with other renewables can improve reliability and reduce costs.
- Novel Applications: Exploring new uses for geothermal energy, such as energy storage and mineral extraction, can further enhance its value.
With continued innovation and investment, geothermal energy can play a pivotal role in meeting the growing energy demand in the US while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing energy security.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌎 Renewable Resource | Geothermal energy is continuously replenished by the Earth’s internal heat. |
| 🏭 Low Emissions | Geothermal power plants produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions. |
| 💡 Baseload Power | Geothermal energy provides a consistent and reliable energy source, available 24/7. |
| 💰 EGS Potential | Enhanced Geothermal Systems can unlock vast resources in previously inaccessible areas. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The key advantage of geothermal energy lies in its reliability. Unlike solar and wind, it provides a constant, 24/7 energy source, making it excellent for baseload power needs.
▼
The majority of geothermal resources in the US are found in the western states, including California, Nevada, Utah, and Oregon, where geological conditions are favorable.
▼
EGS involves creating artificial reservoirs by fracturing hot, dry rocks and injecting water to extract heat, allowing access to geothermal resources in areas without natural hydrothermal systems.
▼
Yes, geothermal energy is environmentally friendly. It produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, requires a small land footprint, and offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
▼
Challenges include high upfront costs, technical complexities, and regulatory hurdles. Overcoming these challenges requires technological innovation, policy support, and public awareness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, geothermal energy in the US represents a vast, untapped potential for sustainable power generation. While challenges remain, ongoing innovation and supportive policies are paving the way for increased utilization of this reliable, low-emission energy source, contributing to a more secure and environmentally responsible energy future.





