Geothermal Energy in the US: Tapping Underground Heat for Homes and Businesses

Geothermal energy in the US offers a sustainable and reliable power source by harnessing the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity and provide direct heating for homes and businesses, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
Harnessing the Earth’s internal heat, geothermal energy in the US: Unlocking the Potential of Underground Heat to Power Homes and Businesses stands as a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, offering a constant, reliable source of power and thermal energy.
Understanding Geothermal Energy in the US
Geothermal energy, derived from the Earth’s internal heat, is a sustainable and renewable resource. In the US, this energy is harnessed through various methods to generate electricity and provide direct heating for homes and businesses. Understanding the basics of geothermal energy is crucial to appreciating its potential and benefits.
What is Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal energy originates from the Earth’s core, which maintains a temperature of approximately 9,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This heat continuously flows to the surface, making it accessible for energy production. Geothermal resources include hydrothermal reservoirs, enhanced geothermal systems (EGS), and geothermal heat pumps.
How is Geothermal Energy Produced?
Geothermal power plants extract hot water or steam from underground reservoirs. This steam powers turbines connected to generators, producing electricity. After use, the cooled water is reinjected back into the reservoir, ensuring sustainability. Direct-use applications involve using geothermal heat for space heating, aquaculture, and industrial processes.
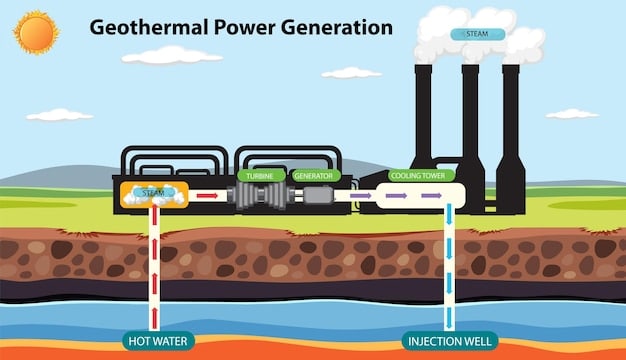
Geothermal energy offers numerous advantages, including:
- Sustainability: Geothermal resources are naturally replenished, ensuring long-term availability.
- Reliability: Unlike solar and wind, geothermal energy is available 24/7, regardless of weather conditions.
- Low Emissions: Geothermal power plants produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel plants.
In summary, geothermal energy in the US is a reliable and environmentally friendly energy source that utilizes the Earth’s natural heat. Its sustainability, reliability, and low emissions make it an attractive alternative to traditional energy sources.
The Current State of Geothermal Energy in the US
Geothermal energy has been utilized in the US for over a century, with significant developments in recent decades. Currently, geothermal power plants and direct-use applications contribute to the nation’s energy mix. Examining the current state of geothermal energy reveals its achievements and areas for growth.
Geothermal Power Generation
The US is a global leader in geothermal power generation, with the majority of its geothermal capacity located in the western states. California, Nevada, Utah, and Oregon are the primary states utilizing geothermal resources for electricity production. The Geysers Geothermal Field in California is one of the world’s largest geothermal complexes.
Direct-Use Applications
Direct-use applications of geothermal energy involve using geothermal heat for various purposes, such as space heating, greenhouse heating, aquaculture, and industrial processes. These applications are widespread across the US, particularly in areas with accessible geothermal resources. Klamath Falls, Oregon, is a notable example of a city heavily reliant on direct-use geothermal energy.
Despite its potential, geothermal energy faces several challenges:
- High Upfront Costs: Construction of geothermal power plants and drilling wells require significant initial investment.
- Geographic Limitations: Geothermal resources are not evenly distributed across the US, limiting its accessibility in certain regions.
- Technological Advancements: Further research and development are needed to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of geothermal technologies.
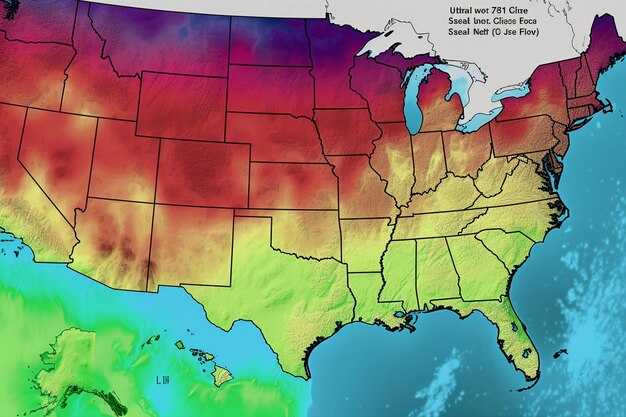
Overall, geothermal energy in the US currently plays a significant role in the nation’s energy landscape, particularly in states with abundant geothermal resources. Overcoming existing challenges and fostering innovation are crucial to expanding its reach and impact.
Benefits of Geothermal Energy for Homes and Businesses
Geothermal energy offers numerous benefits for both residential and commercial applications. From reducing energy costs to minimizing environmental impact, geothermal systems provide a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional heating and cooling methods.
Cost Savings
Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) are highly efficient, using the Earth’s constant temperature to heat and cool buildings. This results in significant energy savings compared to conventional HVAC systems. Homeowners and businesses can reduce their utility bills by leveraging geothermal technology.
Environmental Advantages
Geothermal energy is a clean and renewable resource, producing minimal greenhouse gas emissions. GHPs do not burn fossil fuels, reducing carbon footprint and air pollution. Utilizing geothermal energy contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Reliability and Longevity
Geothermal systems have a long lifespan, with underground components lasting for decades. GHPs require less maintenance than traditional HVAC systems, reducing operational costs and ensuring reliable performance. Geothermal energy provides a stable and consistent energy source, unaffected by weather fluctuations.
Key benefits of geothermal energy for homes and businesses include:
- Reduced energy costs
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Improved indoor air quality
In conclusion, geothermal energy offers substantial benefits for homes and businesses, providing cost savings, environmental advantages, and reliable performance. Its adoption can contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
Technological Advancements in Geothermal Extraction
Technological advancements are continually improving the efficiency and accessibility of geothermal energy extraction. Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) and advanced drilling techniques are expanding the potential of geothermal resources in the US.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS)
EGS technology involves creating artificial fractures in hot, dry rocks deep underground to allow water to circulate and extract heat. This technology opens up geothermal potential in areas without natural hydrothermal reservoirs. EGS is being developed and tested at various sites across the US.
Advanced Drilling Techniques
Advanced drilling techniques, such as horizontal and directional drilling, enable access to geothermal resources in complex geological formations. These techniques improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of geothermal extraction. Research and development efforts are focused on optimizing drilling processes and reducing drilling costs.
Recent technological innovations include:
- High-temperature materials for well construction
- Advanced sensors for reservoir monitoring
- Improved heat exchangers for efficient energy transfer
In summary, technological advancements are crucial to unlocking the full potential of geothermal energy extraction in the US. EGS and advanced drilling techniques are expanding the reach and efficiency of geothermal resources, paving the way for increased adoption and utilization.
The Role of Government Incentives and Policies
Government incentives and policies play a crucial role in promoting the development and adoption of geothermal energy in the US. Financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and research funding are essential to fostering growth in the geothermal sector.
Federal Incentives
The federal government offers various incentives to support geothermal energy, including tax credits, grants, and loan guarantees. These incentives reduce the financial burden of geothermal projects and encourage investment in geothermal technologies. The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and Production Tax Credit (PTC) are key incentives for geothermal power generation.
State Policies
State governments also play a significant role in promoting geothermal energy through policies such as renewable portfolio standards (RPS) and feed-in tariffs. These policies create a supportive regulatory environment for geothermal development and incentivize utilities to incorporate geothermal energy into their energy mix. States like California and Nevada have implemented robust policies to support geothermal energy.
Research and Development Funding
Government funding for research and development is critical to advancing geothermal technologies and reducing costs. The Department of Energy (DOE) supports research initiatives focused on EGS, advanced drilling techniques, and geothermal resource assessment. These efforts accelerate innovation and improve the competitiveness of geothermal energy.
Government support mechanisms include:
- Tax credits and grants
- Loan guarantees
- Renewable portfolio standards
In conclusion, government incentives and policies are essential to driving the growth of geothermal energy in the US. Financial incentives, supportive regulatory frameworks, and research funding create a favorable environment for geothermal development and contribute to a sustainable energy future.
Overcoming Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its potential, geothermal energy faces several challenges that need to be addressed to realize its full potential in the US. Overcoming these challenges and pursuing future opportunities will be critical to expanding the role of geothermal energy in the nation’s energy mix.
Addressing High Upfront Costs
The high upfront costs of geothermal projects can be a barrier to investment. Strategies to reduce costs include technological innovation, streamlined permitting processes, and innovative financing mechanisms. Public-private partnerships can also help share the financial burden and accelerate project development.
Expanding Geographic Reach
Geothermal resources are not evenly distributed across the US, limiting its accessibility in certain regions. EGS technology offers the potential to expand geothermal energy to areas without natural hydrothermal reservoirs. Further research and development are needed to optimize EGS technology and make it more cost-effective.
Future opportunities for geothermal energy include:
- Integration with other renewable energy sources
- Development of hybrid geothermal-solar power plants
- Expansion of direct-use applications
In summary, addressing challenges and pursuing future opportunities are crucial to realizing the full potential of geothermal energy in the US. Overcoming high upfront costs, expanding geographic reach, and fostering innovation will pave the way for increased adoption and utilization of geothermal resources.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🔥 Resource Type | Harnesses Earth’s internal heat for power and direct use. |
| 💰 Cost Savings | Reduces energy bills with efficient heating and cooling. |
| 🌱 Environmentally Friendly | Low emissions and renewable, reduces carbon footprint. |
| 🛠️ Advancements | EGS and drilling innovations expand geothermal potential. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Geothermal energy comes from the Earth’s internal heat. It’s harnessed by drilling wells into underground reservoirs to extract steam or hot water which then powers turbines to generate electricity or provides direct heating for buildings.
▼
Geothermal energy is most prevalent in the western states, particularly in California, Nevada, Utah, and Oregon, where there are significant geothermal resources. These states use geothermal for electricity generation and direct heating.
▼
Geothermal energy is a renewable resource that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, reducing carbon footprint and air pollution. It also reduces reliance on fossil fuels, promoting a more sustainable environment for future generations.
▼
Key challenges include high upfront costs for construction, limited geographic availability of geothermal resources, and the need for technological advancements to improve efficiency and reduce drilling costs for Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS).
▼
Government incentives such as tax credits, grants, and loan guarantees can reduce the financial burden of geothermal projects, encourage investment in geothermal technologies, and create a supportive regulatory environment for geothermal development.
Conclusion
Geothermal energy in the US: Unlocking the Potential of Underground Heat to Power Homes and Businesses represents a vital component of a sustainable energy future. By addressing existing challenges and fostering innovation, the US can harness the full potential of geothermal resources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and advancing environmental stewardship.





