Green Tech Innovations Article – green_tech_greenpowerupdatecom_4_1749971031_67afbf2b_algae_biof.html
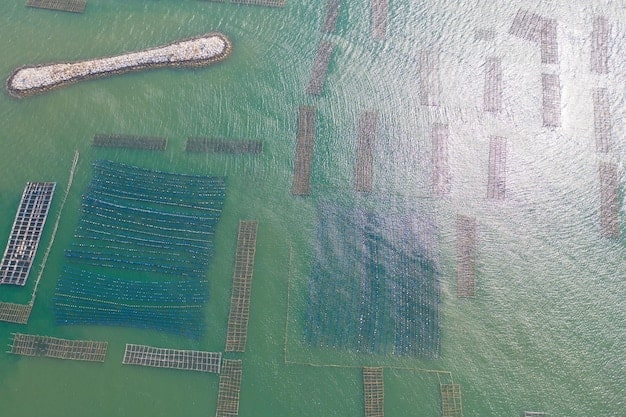

Algae biofuel offers a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, potentially transforming the US transportation sector by 2040 through advanced technology and sustainable practices.
The quest for sustainable energy sources has led researchers to explore the potential of algae as a biofuel. Could the Algae Biofuel Revolution: Can This Promising Technology Replace Fossil Fuels in the US Transportation Sector by 2040? The answer may be closer than we think.
Understanding Algae Biofuel: A Promising Alternative
Algae biofuel is garnering significant attention as a potential replacement for fossil fuels. Its rapid growth rate and ability to thrive in diverse environments make it a compelling candidate for sustainable energy production.
But what exactly is algae biofuel, and why is it considered such a promising alternative?
What is Algae Biofuel?
Algae biofuel is a type of biofuel derived from algae. Unlike traditional biofuels that use food crops like corn or soybeans, algae biofuel utilizes microorganisms that can efficiently convert sunlight and carbon dioxide into lipids, which can then be processed into biodiesel, bio gasoline, and bio jet fuel.
Why Algae?
Algae offer several advantages over other biofuel sources. They have a higher lipid content compared to many other biomass sources, leading to greater fuel production per unit area. Additionally, algae can be grown on non-arable land and in wastewater, reducing competition with food crops and minimizing environmental impact.
- High lipid content for efficient fuel production.
- Can be grown on non-arable land.
- Utilizes wastewater, reducing freshwater consumption.
- Reduces carbon emissions.
In conclusion, algae biofuel represents a significant opportunity to create a sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation sector. Its unique properties and cultivation advantages make it a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, paving the way for a greener future.

The Current State of Algae Biofuel Technology
The development of algae biofuel technology is still in its early stages, but significant progress has been made in recent years. Research institutions and private companies are actively exploring various methods to enhance the efficiency and scalability of algae biofuel production.
Let’s delve into the current state of this exciting field.
Cultivation Methods
Algae cultivation methods can be broadly categorized into open ponds and photobioreactors. Open ponds are cost-effective but are susceptible to contamination and environmental fluctuations. Photobioreactors, on the other hand, offer better control over cultivation conditions but are more expensive to construct and operate.
Conversion Technologies
Once algae biomass is harvested, it needs to be converted into biofuel. Several conversion technologies are being developed, including lipid extraction, hydrothermal liquefaction, and anaerobic digestion. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, cost, and environmental impact.
- Lipid extraction: Separates lipids from algae biomass for biodiesel production.
- Hydrothermal liquefaction: Converts entire algae biomass into bio-crude oil under high temperature and pressure.
- Anaerobic digestion: Decomposes algae biomass in the absence of oxygen to produce biogas.
- Gasification: Converts algae biomass into syngas, which can be further processed into various fuels.
In summary, continuous innovation in cultivation and conversion technologies is essential for making algae biofuel economically competitive and environmentally sustainable. The choice of method depends on specific goals and available resources.
Economic Viability: Can Algae Biofuel Compete?
One of the biggest challenges facing the algae biofuel revolution is its economic viability. The cost of producing algae biofuel is currently higher than that of fossil fuels and other biofuels. Addressing this issue is crucial for the widespread adoption of algae biofuel in the US transportation sector.
So, what factors influence the economic viability of algae biofuel?
Reducing Production Costs
Reducing production costs is paramount for making algae biofuel competitive. This can be achieved through advancements in cultivation and conversion technologies, as well as optimizing resource utilization and reducing waste.
Government Incentives and Policies
Government incentives and policies play a critical role in supporting the development and deployment of algae biofuel. Tax credits, subsidies, and mandates for renewable fuels can help level the playing field and encourage investment in algae biofuel technologies.
Algae biofuel is a fuel substitute that could boost the American economy. These are some elements that influence the price of this new and renewable fuel type:
- Government subsidies.
- The need to reduce carbon emissions.
- Advancements in technology.
In conclusion, cost-effective production, combined with supportive government policies, can pave the way for algae biofuel to compete with fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable and economically viable transportation sector.
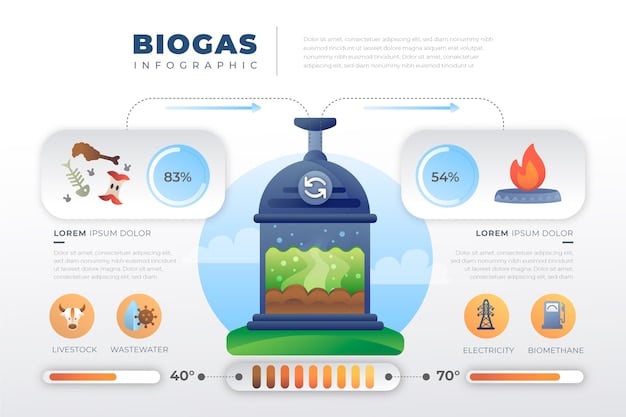
Environmental Impact: A Sustainable Solution?
Algae biofuel is often touted as a sustainable solution to reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector. Compared to fossil fuels, algae biofuel offers several environmental advantages, including lower carbon emissions and reduced land use.
But is algae biofuel truly a sustainable solution?
Reducing Carbon Emissions
Algae biofuel can significantly reduce carbon emissions by capturing carbon dioxide during cultivation. The carbon dioxide can be sourced directly from the atmosphere or from industrial sources, such as power plants, further reducing the carbon footprint.
Minimizing Land Use
Unlike traditional biofuels that require arable land, algae can be grown on non-arable land, minimizing competition with food crops. This makes algae biofuel a more sustainable option for meeting transportation fuel demands without compromising food security.
The environmental advantages of algae cultivation are varied. Some of them are:
- Reduction of land use.
- Lower carbon emissions.
- Uses wastewater.
In summary, reducing carbon emissions and minimizing land use, algae biofuel presents a promising pathway toward a more sustainable and environmentally responsible US transportation sector.
Challenges and Opportunities on the Road to 2040
While algae biofuel holds great promise, several challenges need to be addressed to ensure its widespread adoption by 2040. These challenges range from technical hurdles to regulatory barriers, but they also present significant opportunities for innovation and growth.
What are some of the key challenges and opportunities?
Technical Challenges
Technical challenges include improving the efficiency of algae cultivation and conversion processes, as well as scaling up production to meet the demands of the transportation sector. Research and development efforts are needed to overcome these hurdles and optimize algae biofuel production.
Regulatory and Policy Barriers
Regulatory and policy barriers can hinder the deployment of algae biofuel. Clear and consistent regulations are needed to streamline the approval process for algae biofuel projects and encourage investment in the industry.
There are considerable opportunities for those who choose to work with this fuel type. Among them are:
- Scale up production.
- Streamline the process and obtain permits quicker.
- Improve algae cultivation.
In conclusion, overcoming technical and regulatory challenges requires collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders. By addressing these challenges and seizing the opportunities for innovation, algae biofuel can play a significant role in transforming the US transportation sector by 2040.
Policy and Investment: Fueling the Algae Biofuel Revolution
Government policy and private investment are critical drivers of the algae biofuel revolution. Supportive policies can create a favorable environment for algae biofuel development, while strategic investments can accelerate the commercialization of algae biofuel technologies.
How can policy and investment support the algae biofuel revolution?
Government Support
Government support can take various forms, including tax incentives, research grants, and loan guarantees. These measures can help reduce the financial risks associated with algae biofuel projects and attract private investment.
Private Sector Investment
Private sector investment is essential for scaling up algae biofuel production and deploying commercial-scale facilities. Venture capital firms, energy companies, and agricultural businesses can play a key role in funding algae biofuel projects and bringing them to market.
These points could help boost the growth of algae biofuel:
- Tax incentives.
- Research grants.
- Loan guarantees.
In summary, government policy and private investment are essential for fueling the algae biofuel revolution. Combining these forces can drive innovation, reduce costs, and pave the way for the widespread adoption of algae biofuel in the US transportation sector by 2040.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌱 Sustainability | Algae biofuel reduces carbon emissions. |
| 💰 Economic Viability | Reducing production costs is vital. |
| 🔬 Technology | Innovations improve fuel production. |
| 政策 Investment | Fueling the algae biofuel revolution. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Algae Biofuel
▼
Algae biofuel is a renewable fuel derived from algae biomass. It’s created by cultivating algae, extracting the oils, and then processing these oils into biodiesel or other biofuels.
▼
Algae biofuel reduces carbon emissions compared to fossil fuels. It also doesn’t compete with food crops and can be grown using wastewater, minimizing land and water usage.
▼
Currently, algae biofuel is more expensive than traditional fuels. Ongoing research and technological advances aim to reduce production costs, making it more economically competitive.
▼
Government support through incentives and funding, and private investment in technology and infrastructure are crucial for scaling up algae biofuel production and driving down costs.
▼
Challenges include reducing production costs, improving algae cultivation and conversion efficiency, and addressing regulatory barriers to facilitate commercial deployment and faster adoption.
Conclusion
The Algae Biofuel Revolution presents a promising pathway toward a sustainable future for the US transportation sector. While challenges remain, ongoing innovation, supportive policies, and strategic investments can unlock the full potential of algae biofuel, paving the way for a cleaner, more secure energy future by 2040.
“`
f”* IMPORTANTE – DESCRIÇÃO DO SITE: We share the latest news on how AI and Machine Learning are transforming industries and our way of life.”





